COVID-19 Detection from Spectral Signature
Overview
We developed a novel spectroscopic approach for detecting COVID-19 from saliva samples using absorption and emission spectroscopy. Our method analyzes spectral signatures to identify COVID-19 infection without requiring complex sample preparation or reagents, achieving high classification accuracy through advanced machine learning techniques.
Technical Details
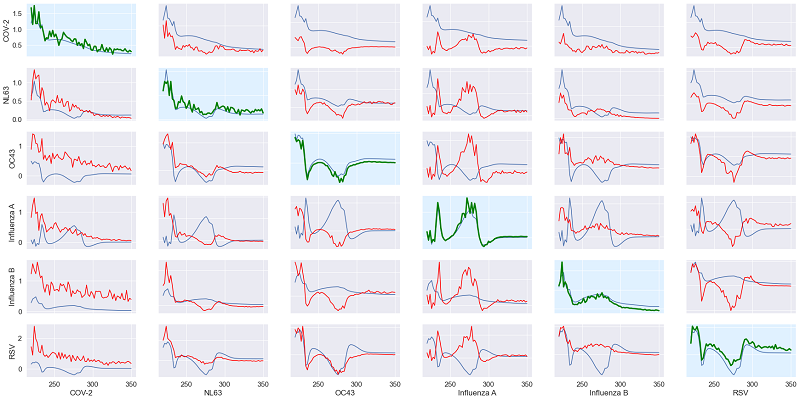
We implemented a comprehensive spectral analysis pipeline that processes both absorption and emission spectroscopy data from saliva samples. The system collects spectral signatures by directing light signals at saliva samples and analyzing the resulting patterns. Through spectral unmixing techniques, we identified distinct endmembers within the signatures, revealing molecular composition changes associated with COVID-19 infection.
Implementation
Using Python and specialized spectral analysis libraries, we processed raw spectroscopic data collected from the University of Arizona. We developed novel spectral augmentation strategies to simulate diverse spectral signatures, generating thousands of synthetic samples for robust model training. This augmented dataset significantly improved our classification performance and model generalization. The implementation included sophisticated signal processing algorithms for both real and simulated data, spectral unmixing techniques, and advanced machine learning models. Our augmentation approach considered various environmental factors and sample conditions to create realistic synthetic spectra.
Key Achievements
Our research demonstrated significant success in COVID-19 detection through spectral analysis, achieving robust classification between positive and negative samples. The combination of real and simulated data enabled us to train more reliable models despite limited initial samples. The system provides a rapid, non-invasive method for COVID-19 screening that complements existing diagnostic tools.
Impact
This research advances spectroscopic disease detection by providing a novel approach to COVID-19 screening. The method offers rapid results, non-invasive sample collection, and potential for high-throughput screening. Our collaboration with Lightsense Technology demonstrates the commercial viability of spectroscopic COVID-19 detection.
Future Directions
We plan to optimize the spectral acquisition process, improve classification accuracy through advanced AI techniques, and develop a portable device for point-of-care testing. Future work will focus on validating the system across larger patient populations and different viral variants, while further refining our spectral augmentation strategies.
Project Links
-
Source Code: GitHub Repository
-
Live Demo: Project Website